Gasoline Direct Injection
Introduction
Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI), also known as Petrol Direct Injection, is a technology used in internal combustion engines to deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber of each cylinder, rather than into the intake manifold. This technology has been widely adopted in the automotive industry due to its potential for increased fuel efficiency and power output.
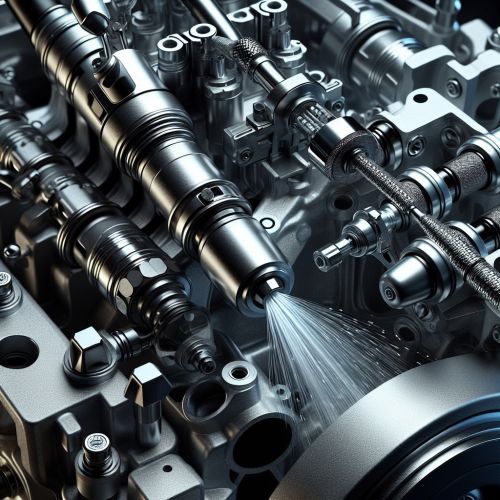

History
The concept of direct fuel injection has been around since the early 20th century, with the first patent for a GDI system being filed by French inventor Léon Levavasseur in 1902. However, it wasn't until the late 20th century that GDI technology became widely used in passenger vehicles, with the Mitsubishi GDI engine, introduced in 1996, being the first mass-produced GDI engine.
Working Principle
In a GDI system, fuel is delivered directly into the combustion chamber of each cylinder, bypassing the intake manifold. This allows for more precise control over the fuel-air mixture, resulting in improved combustion efficiency. The fuel is injected at high pressure, which promotes better atomization and mixing with the air in the cylinder. This leads to a more complete combustion process, which can improve power output and reduce emissions.
Advantages
There are several advantages to using GDI technology in an internal combustion engine. These include increased fuel efficiency, improved power output, and reduced emissions. The precise control over the fuel-air mixture that GDI allows can lead to a more complete combustion process, which can improve power output and reduce emissions. Additionally, because fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber, there is less risk of fuel being wasted through evaporation in the intake manifold.
Disadvantages
Despite its advantages, GDI technology also has some disadvantages. One of the main ones is the potential for increased particulate emissions, due to the high pressure injection of fuel. Additionally, GDI engines can be more expensive to manufacture and maintain than traditional port fuel injection engines, due to the need for high pressure fuel pumps and injectors.
Future Developments
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, so too does GDI technology. One of the main areas of research is in reducing the particulate emissions associated with GDI engines. This is being achieved through the development of new injection strategies and technologies, such as the use of multiple injections per combustion cycle.
