Spacecraft: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "== Introduction == A spacecraft is a vehicle designed for travel or operation in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communication, earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. thumb|center|A spacecraft in outer space, with Earth visible in the background.|class=only_on_mobile Image:Detail-30271.jpg|thumb|center...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
[[Image:Detail- | A [[Spacecraft|spacecraft]] is a vehicle designed for travel or operation in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communication, earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. | ||
[[Image:Detail- | |||
[[Image:Detail-24484.jpg|thumb|center|An image of a spacecraft in outer space.|class=only_on_mobile]] | |||
[[Image:Detail-24485.jpg|thumb|center|An image of a spacecraft in outer space.|class=only_on_desktop]] | |||
== History == | == History == | ||
[[Image:Detail- | The concept of a spacecraft has been prevalent in science fiction long before the practical application of the technology was viable. The first significant step towards actual space travel came with the launching of the [[Sputnik 1|Sputnik 1]] by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957. This was the first artificial satellite to orbit the earth, marking the beginning of the space age. | ||
[[Image:Detail- | |||
== Design and Structure == | |||
The design and structure of a spacecraft can vary greatly depending on its purpose. Some spacecraft are designed to remain in space indefinitely, while others are designed for re-entry and landing. The basic components of a spacecraft include the payload, the propulsion system, the power source, the guidance system, and the communication system. | |||
[[Image:Detail-24486.jpg|thumb|center|An image of the different components of a spacecraft.|class=only_on_mobile]] | |||
[[Image:Detail-24487.jpg|thumb|center|An image of the different components of a spacecraft.|class=only_on_desktop]] | |||
=== Payload === | |||
The payload is the part of the spacecraft that carries out the mission. This can include scientific instruments, communications equipment, or even astronauts in the case of manned missions. The payload is often the most expensive part of the spacecraft and is designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space. | |||
=== Propulsion System === | |||
The propulsion system is what moves the spacecraft. This can be a chemical rocket, an ion drive, or even a solar sail. The choice of propulsion system depends on the mission requirements and the distance to be traveled. | |||
=== Power Source === | |||
The power source provides the energy needed for the spacecraft's systems to function. This can be solar panels, nuclear reactors, or batteries. The choice of power source depends on the distance from the sun and the power requirements of the spacecraft. | |||
=== Guidance System === | |||
The guidance system is what controls the spacecraft's movements. This can be a simple system of thrusters, or a complex system of gyroscopes and computers. The guidance system must be able to withstand the harsh conditions of space and function without human intervention. | |||
=== Communication System === | |||
The communication system is what allows the spacecraft to send and receive information. This can be a simple radio transmitter, or a complex system of antennas and computers. The communication system must be able to withstand the harsh conditions of space and function without human intervention. | |||
[[Image:Detail-24488.jpg|thumb|center|An image of a spacecraft communication system.|class=only_on_mobile]] | |||
[[Image:Detail-24489.jpg|thumb|center|An image of a spacecraft communication system.|class=only_on_desktop]] | |||
== Types of Spacecraft == | |||
There are many different types of spacecraft, each designed for a specific purpose. These include satellites, probes, rovers, space stations, and manned spacecraft. | |||
=== Satellites === | |||
[[Satellites|Satellites]] are spacecraft that orbit around the earth or another celestial body. They are used for a variety of purposes, including communication, earth observation, meteorology, and navigation. | |||
=== Probes === | |||
[[Probes|Probes]] are spacecraft that are sent to explore other celestial bodies. They are often unmanned and carry scientific instruments to gather data. | |||
=== Rovers === | |||
[[Rovers|Rovers]] are a type of probe that can move around on the surface of a celestial body. They are used to explore the surface and gather data. | |||
=== Space Stations === | |||
[[Space Stations|Space Stations]] are large spacecraft that remain in orbit around the earth. They are used for scientific research and as a base for other space missions. | |||
=== Manned Spacecraft === | |||
[[Manned Spacecraft|Manned spacecraft]] are designed to carry humans into space. They are used for exploration, research, and space tourism. | |||
[[Image:Detail- | [[Image:Detail-24490.jpg|thumb|center|An image of a manned spacecraft.|class=only_on_mobile]] | ||
[[Image:Detail- | [[Image:Detail-24491.jpg|thumb|center|An image of a manned spacecraft.|class=only_on_desktop]] | ||
== | == Future of Spacecraft == | ||
[[Image:Detail- | The future of spacecraft is a topic of much speculation and research. With advancements in technology, the possibilities for space exploration are expanding. Potential future developments include reusable spacecraft, interplanetary travel, and even interstellar travel. | ||
[[Image:Detail- | |||
[[Image:Detail-24492.jpg|thumb|center|An image of a futuristic spacecraft.|class=only_on_mobile]] | |||
[[Image:Detail-24493.jpg|thumb|center|An image of a futuristic spacecraft.|class=only_on_desktop]] | |||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Space Exploration]] | * [[Space Exploration]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Space Technology]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Space Missions]] | ||
[[Category:Spacecraft]] | [[Category:Spacecraft]] | ||
[[Category:Space Exploration]] | [[Category:Space Exploration]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Space Technology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:23, 30 October 2023
Introduction
A spacecraft is a vehicle designed for travel or operation in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communication, earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo.


History
The concept of a spacecraft has been prevalent in science fiction long before the practical application of the technology was viable. The first significant step towards actual space travel came with the launching of the Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957. This was the first artificial satellite to orbit the earth, marking the beginning of the space age.
Design and Structure
The design and structure of a spacecraft can vary greatly depending on its purpose. Some spacecraft are designed to remain in space indefinitely, while others are designed for re-entry and landing. The basic components of a spacecraft include the payload, the propulsion system, the power source, the guidance system, and the communication system.
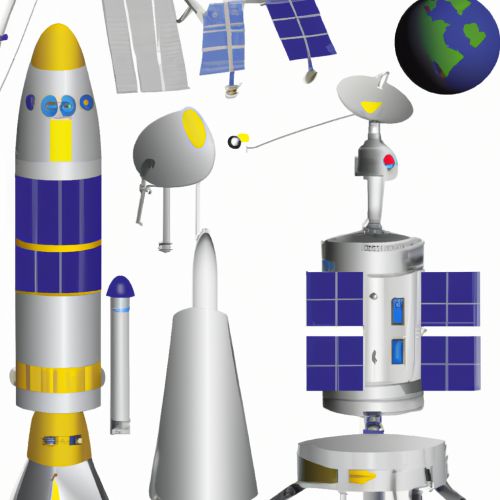
Payload
The payload is the part of the spacecraft that carries out the mission. This can include scientific instruments, communications equipment, or even astronauts in the case of manned missions. The payload is often the most expensive part of the spacecraft and is designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space.
Propulsion System
The propulsion system is what moves the spacecraft. This can be a chemical rocket, an ion drive, or even a solar sail. The choice of propulsion system depends on the mission requirements and the distance to be traveled.
Power Source
The power source provides the energy needed for the spacecraft's systems to function. This can be solar panels, nuclear reactors, or batteries. The choice of power source depends on the distance from the sun and the power requirements of the spacecraft.
Guidance System
The guidance system is what controls the spacecraft's movements. This can be a simple system of thrusters, or a complex system of gyroscopes and computers. The guidance system must be able to withstand the harsh conditions of space and function without human intervention.
Communication System
The communication system is what allows the spacecraft to send and receive information. This can be a simple radio transmitter, or a complex system of antennas and computers. The communication system must be able to withstand the harsh conditions of space and function without human intervention.


Types of Spacecraft
There are many different types of spacecraft, each designed for a specific purpose. These include satellites, probes, rovers, space stations, and manned spacecraft.
Satellites
Satellites are spacecraft that orbit around the earth or another celestial body. They are used for a variety of purposes, including communication, earth observation, meteorology, and navigation.
Probes
Probes are spacecraft that are sent to explore other celestial bodies. They are often unmanned and carry scientific instruments to gather data.
Rovers
Rovers are a type of probe that can move around on the surface of a celestial body. They are used to explore the surface and gather data.
Space Stations
Space Stations are large spacecraft that remain in orbit around the earth. They are used for scientific research and as a base for other space missions.
Manned Spacecraft
Manned spacecraft are designed to carry humans into space. They are used for exploration, research, and space tourism.


Future of Spacecraft
The future of spacecraft is a topic of much speculation and research. With advancements in technology, the possibilities for space exploration are expanding. Potential future developments include reusable spacecraft, interplanetary travel, and even interstellar travel.


