Elements and Principles of Design: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "== Elements and Principles of Design == The field of design encompasses a variety of disciplines, each with its own set of rules and guidelines. However, there are fundamental elements and principles that are universally recognized across all design fields. These elements and principles serve as the foundation for creating visually appealing and functional designs. === Elements of Design === The elements of design are the basic components or building blocks used to cr...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
A line is a continuous mark made on a surface by a moving point. It can vary in width, direction, and length. Lines can be horizontal, vertical, diagonal, or curved, and they can be used to define shapes, create textures, and convey movement. Lines can also be used to guide the viewer's eye through a composition. | A line is a continuous mark made on a surface by a moving point. It can vary in width, direction, and length. Lines can be horizontal, vertical, diagonal, or curved, and they can be used to define shapes, create textures, and convey movement. Lines can also be used to guide the viewer's eye through a composition. | ||
[[Image:Detail-91633.jpg|thumb|center|Various types of lines drawn on a white background, including straight, curved, and zigzag lines.|class=only_on_mobile]] | |||
[[Image:Detail-91634.jpg|thumb|center|Various types of lines drawn on a white background, including straight, curved, and zigzag lines.|class=only_on_desktop]] | |||
==== Shape ==== | ==== Shape ==== | ||
Latest revision as of 09:01, 20 June 2024
Elements and Principles of Design
The field of design encompasses a variety of disciplines, each with its own set of rules and guidelines. However, there are fundamental elements and principles that are universally recognized across all design fields. These elements and principles serve as the foundation for creating visually appealing and functional designs.
Elements of Design
The elements of design are the basic components or building blocks used to create a visual composition. These elements include:
Line
A line is a continuous mark made on a surface by a moving point. It can vary in width, direction, and length. Lines can be horizontal, vertical, diagonal, or curved, and they can be used to define shapes, create textures, and convey movement. Lines can also be used to guide the viewer's eye through a composition.
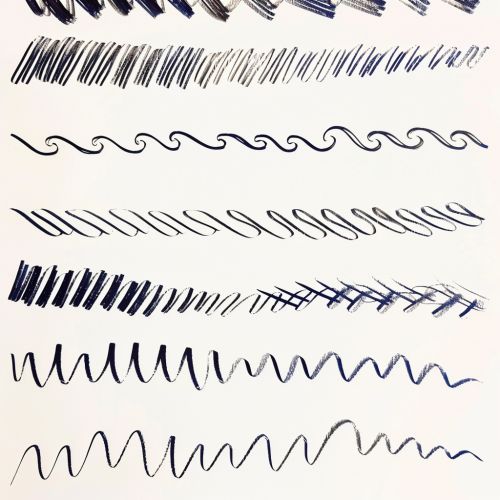

Shape
Shapes are defined by boundaries, such as lines or colors, and can be geometric (e.g., circles, squares, triangles) or organic (e.g., natural, free-form shapes). Shapes are two-dimensional and can be used to create patterns, textures, and compositions.
Form
Form refers to the three-dimensional quality of an object, which includes its volume and mass. Forms can be geometric (e.g., cubes, spheres, pyramids) or organic (e.g., natural, free-form forms). Form is often used in sculpture and architecture to create depth and dimension.
Space
Space refers to the area around, between, and within objects. It can be positive (the area occupied by an object) or negative (the area around and between objects). Space can be used to create a sense of depth, perspective, and balance in a composition.
Texture
Texture refers to the surface quality of an object, which can be tactile (physical texture) or visual (implied texture). Texture can add interest and depth to a design and can be created using various techniques, such as hatching, stippling, and cross-hatching.
Color
Color is produced when light, striking an object, is reflected back to the eye. It has three main properties: hue (the name of the color), value (the lightness or darkness of the color), and intensity (the brightness or dullness of the color). Color can evoke emotions, create emphasis, and establish harmony in a design.
Value
Value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color. It is an important element in creating contrast, depth, and emphasis in a design. Value can be manipulated through shading, highlighting, and the use of different tones and tints.
Principles of Design
The principles of design are the guidelines used to organize and arrange the elements of design. These principles include:
Balance
Balance refers to the distribution of visual weight within a composition. It can be symmetrical (evenly balanced) or asymmetrical (unevenly balanced). Balance creates a sense of stability and harmony in a design.
Contrast
Contrast involves the use of opposing elements, such as light and dark, rough and smooth, or large and small, to create visual interest and emphasis. Contrast helps to draw attention to important areas of a design and can create a dynamic composition.
Emphasis
Emphasis is the focal point of a design, where the viewer's attention is drawn. It can be achieved through the use of contrast, color, size, and placement. Emphasis helps to create a hierarchy of importance within a composition.
Movement
Movement refers to the way the viewer's eye is guided through a composition. It can be created through the use of lines, shapes, colors, and textures. Movement helps to create a sense of flow and direction in a design.
Pattern
Pattern involves the repetition of elements, such as shapes, lines, or colors, to create a cohesive and organized design. Patterns can be regular (consistent and predictable) or irregular (random and varied). Patterns add rhythm and structure to a composition.
Rhythm
Rhythm is the repetition of visual elements to create a sense of movement and harmony. It can be achieved through the use of patterns, lines, shapes, and colors. Rhythm helps to create a cohesive and dynamic design.
Unity
Unity refers to the sense of cohesion and harmony within a design. It is achieved through the consistent use of elements and principles, such as color, shape, and pattern. Unity helps to create a sense of completeness and wholeness in a composition.
Proportion
Proportion refers to the relationship between the sizes of different elements within a composition. It can be used to create emphasis, balance, and harmony. Proportion helps to establish a sense of scale and hierarchy in a design.
Variety
Variety involves the use of different elements and principles to create visual interest and prevent monotony. It can be achieved through the use of contrasting colors, shapes, textures, and patterns. Variety adds complexity and richness to a design.
